How CBDCs Could Disrupt the $700 Billion Global Remittance Industry
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) offer the real promise of making remittances safer, faster, and cheaper - although a lot of groundwork is still needed.
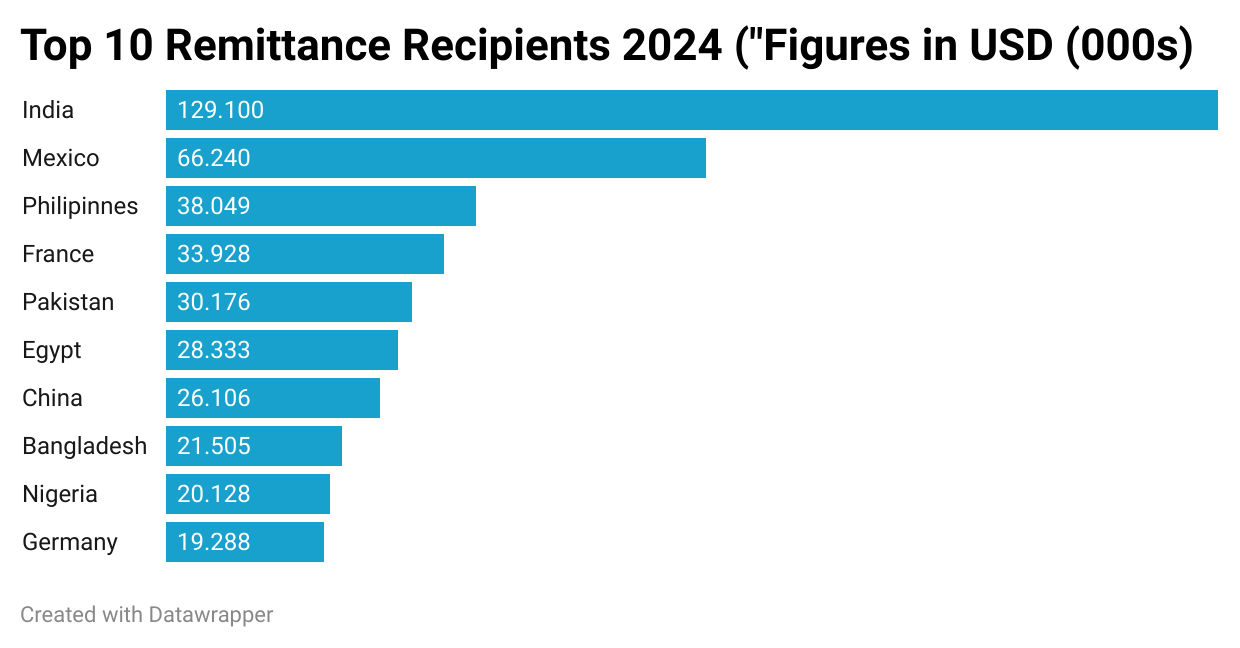
According to The World Bank, remittance flows into Low and Middle Income Countries (LMICs) hit $780 billion in 2024. The value of the global remittances industry is believed to be even higher, given that flows through informal channels are not officially accounted for. The importance of remittances cannot be overstated – remittances provide a lifeline for millions of families. The illustration below shows the top 10 remittance recipients in 2024, and the corresponding value of the remittances.
Over the years, the value of remittances has grown, a trend that is partially attributed to the affordances of fintech, which make transfers faster and cheaper. These developments notwithstanding, CBDCs can bring a whole new level of disruption. What follows is an exploration of how CBDCs could reshape the global remittance landscape, and the relevant challenges.
The High Cost of Money Transfers Today
Globally, the cost of sending remittances is an average of 6.62% of the total amount sent (The World Bank, 2024). The industry is dominated by traditional players such as MoneyGram and Western Union, who charge relatively high fees. Among other pain points of this system of transfers is the issue of hidden costs in exchange rates, delays in certain cases, and vulnerability to errors and fraud. The graphical illustration below shows the remittance transaction costs by region. Target 10c of UNSDG 10 aims to bring down the cost of migrant remittances to 3% by 2030. From the graph, the current costs are way above the 3% target.
CBDCs – What are they, and what is their Influence?
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are government-issued digital currencies backed by a central bank. The main advantages of CBDCs for remittances are;
Lower transaction costs. CBDCs have the potential to reduce remittance costs by facilitating direct transfers between the central banks of different countries. This lowers transaction fees.
Faster cross-border settlements. CBDCs reduce settlement risks and the reliance on financial intermediaries.
Potentially greater transparency. CBDCs operate on distributed ledger technology, allowing for traceability of transactions and increased transparency.
Direct peer-to-peer transfers. By facilitating direct transfers, CBDCs reduce intermediaries, thus, facilitating direct peer-to-peer transfers.
The Early Movers
India
Launched in December 2022, India’s e-rupee has since been linked with diaspora remittances. A key reason behind this development was to reduce the transaction costs of remittances, in line with Target 10c of UNSDG 10. According to India’s Economic Affairs Secretary, Ajay Seth, the e-rupee can help halve the cost of cross-border remittances.
Nigeria
Like the case of India, Nigeria’s e-Naira is aimed at reducing the cost of remittance transactions and in addition, promoting financial inclusion. The infrastructure of the e-Naira adopts distributed ledger technology which promotes financial inclusion through streamlining account opening and onboarding processes.
The Bahamas
The Bahamas launched its CBDC, the sand dollar, in October 2020, making it the world’s first digital currency. This has since facilitated low-cost regional and local transactions.
Some Noteworthy Stumbling Blocks
Despite the potential of CBDCs to significantly revolutionize the global remittance industry, their adoption and implementation is defined by certain challenges. For one, adoption itself is a challenge as many families and workers may lack smartphones or digital wallets. Another challenge stems from the issue of trust deficit, as potential users may fear financial surveillance. Third, given that CBDCs are a relatively recent phenomena, there exist technical challenges such as the interoperability between different countries, that are yet to be solved. Finally, regulatory barriers remain a hurdle as cross-border regulations are still catching up.
Conclusion
CBDCs offer the real promise of making remittances safer, faster, and cheaper. Nonetheless, there is still a lot of groundwork needed. Done correctly, these digital currencies could revolutionize the movement of money across borders.